
Legal Provisions means any federal, state, local or foreign statute, law, regulation, judgment, order or decree of any Governmental Entity. It helps to safeguard your invention and protect any product, design or process that meets certain specifications according to its originality, practicality, suitability, and utility. Every county in the world make Legal provision to register and obtain patent and so is done of local landraces in Nepal which is included under Section 3 of Seed Act 2069.
For Registration: Rule 11 and Rule 12
11.1 The producer should compulsorily register the seeds of new races before production and marketing.
12.2 To register local landraces of Nepal, the seed producer should give an application in the given format to the sub-committee.


12.3 The sub-committee should examine the applications received and investigate it properly before submitting it to the committee.
For obtaining patent: Rule 14
14.1 If the seed producer wants to get patent over their seeds, they should submit an application as given.
14.2 After application is received as per Sub-rule 1 of rule 14, the committee should provide patent to the producer/owner as per Schedule 5 keeping in view the usefulness and importance of the seed.
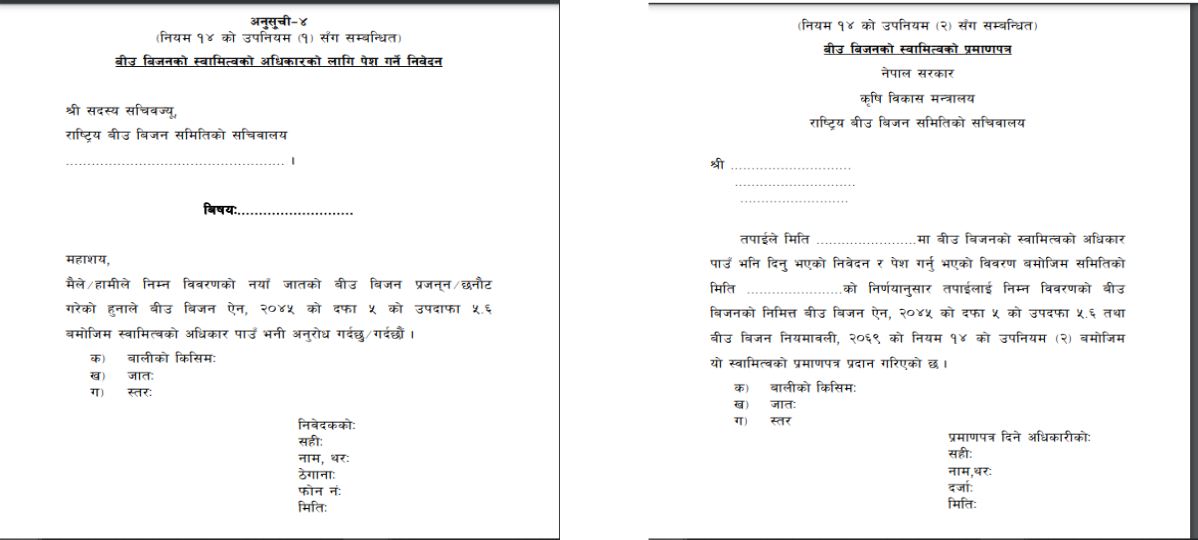
14.3 In case of two or more owners/producers claiming patent over same type of landrace, the one who has given application first and whose seed has been registered first will be prioritized.
Patent Law:
Patent law is the collection of laws and rules that protect the patentable inventions, thus implying not every invention is patentable. For an invention to be granted patent rights, the invention must meet the following requirements:
It should involve a process or the method;
It must show an element of novelty;
It must involve an inventive or non-obvious step;
It must be capable of industrial application.
Patent law in Nepal
The Patent, Design and Trademark Act, 2022 B.S. (PDT Act) is the governing law for the registration and protection of patents in Nepal. Since Nepal is also a signatory to the Paris Convention for the Protection of Industrial Property 1883, patents registered in Nepal are provided with international protection.
The PDT Act requires that, to acquire patent protection the invention must be registered at the Department of Industry (DOI). And for the registration, the person should apply to the DOI disclosing the process, formula and everything that was required in making the final product in itself. Upon receiving an application, the DOI conducts all the required investigation as to whether the invention is novel or not, and whether it is useful to the general public or not, and thereafter decides whether or not to register such patent.
Important of Patent:
It can help safeguard your invention.
It can protect any product, design or process that meets certain specifications according to its originality, practicality, suitability, and utility.
In most cases, a patent can protect an invention for up to 20 years. This time period starts soon as you file your patent.
Healthy market position: your new idea could be a great differentiator among competitors
Favorable image: you’ll be seen as thought leaders, building credibility and your reputation
Higher return on your investment: applying for a patent could cost in excess of $10,000, and you can commercialize the concept for returns
License or sell the invention: If you don’t have the time or means to exploit the invention, sell it for a new revenue stream
Raise funds for your business: If you have a patent that allows you to gain market share, investors will be interested
Increase your negotiating power: If you have a patent pending, this may help you when developing new contracts
Disadvantage of patent:
Applying for a patent can be a very time consuming and lengthy process (typically three to four years), markets may change or technology may overtake your invention by the time you get a patent.
Cost – It will cost you money whether you are successful or not – the application, searches for existing patents and a patent attorney’s fees can all contribute to a reasonable outlay. The potential for making a profit should outweigh the time, effort and money it takes to get and maintain a patent.
You’ll need to remember to pay your annual fee or your patent will lapse.
You’ll need to be prepared to defend your patent. Taking action against an infringer can be very expensive. On the other hand, a patent can act as a deterrent, making defence unnecessary.
PROCEDURE TO GET PATENT
Right over the patent:
Any person, willing to have rights on any patent has to register such patent under the Patent Design and Trademark Act.
Any patent registered in the name of any person shall not be copied use used or utilized without the patentee’s written consent.
Ownership of a patent can be transferred in any way to any person as movable property.
If anybody does or attempt to do so or encourage to do any work against these rights of patentee may be punished with a fine by the order of Department and all the materials related with such offence shall be confiscated.
Apply for acquiring patent right:
Person willing to patent registered in his own name shall have to apply to the Department with following information including all other evidence
Name, address and profession of inventor.
In the case of the invention not invented by the applicant himself, the conditions acquiring such right from inventor by the applicant,
Method of operation or utilization of such invention
Principle or formula, if such patent is based on any principle or formula
Drawings and sketch of invention (if necessary)
Prescribed application fee as mention in schedule
If it has already been registered in the name of other.
If the patent asked to be registered is not invented by the applicant himself and he has not acquired the right from the inventor
If the patent asked to be registered is found to cause adverse effect in health , conduct or morale or people in general or in the national interest
If it violates any prevailing laws of Nepal.
Department upon submission of an patent application examine the invention whether it is new or not, it is useful to the people in general or not
If it deems necessary, Department takes the advice of experts of related field
Basically, Department fallow the principle of Novelty, Industrial applicability, and Inventive step to examine
If Department found the patent application is patentable after examination provide certificates to the applicant
Applicant shall pay a registration fee as prescribed in schedule.
Department shall publish all patents, except those to be kept secret for national interest in journal
Anybody willing to see or take a copy of the statement, drawing or sketch of a patent published in journal may see or take a copy of such patent document on payment of a fee as prescribed.
Opposition:
If anybody has any complain upon any patent he may lodge such complains to the Department within thirty-five days from the date on which the patent is seen or a copy of such patent document is taken.
Upon receipt of the complain Department take necessary action through an investigation.
Term and renewal
Patentee shall have his right on the patent for a period of seven years from the date of registration.
The patentee shall renew the patent within 35 days from date of expiry having paid the fee mention in schedule.
Renewal of a patent may be made for two times of seven years.









