
Seed priming is a pre-sowing technique in which seeds are moderately hydrated to the point where pre germination metabolic processes begin without actual germination. Seeds are then reduced to near their actual weight for normal handling.
Understanding the Process of Seed Priming :
Seed priming is a process of regulating the germination process by managing the temperature and seed moisture content, the seed is taken through the first biochemical processes within the initial stages of germination. The priming process regulates the seed’s temperature and moisture content, bringing the seed closer to the point of germination. The process involves advancing the seed to an equal stage of the germination process, to enable fast and uniform emergence when planted.
Important points:
- Priming allows some of the metabolic processes for germination to occur without germination.
- This prevents the seeds from absorbing enough water for radical protrusion.
- This hydration is sufficient to permit the pre-germination metabolic process but insufficient to allow radical protrusion from the seed coat.
Advantage of Seed priming :
- It decreases the time of germination.
- Increase the rate of germination.
- Uniform germination.
- Crops can compete with the weeds more effectively.
- Eliminate or greatly reduce the occurrence of soil-borne fungus.
- Improve seed performance stress conditions.
Seed priming methods: There are 4 common methods for priming seeds.
1.Hydro-priming:
Hydro priming involves soaking seeds in water and drying back to storage moisture before sowing of the seeds. This decreases the time that the seed spends in the seedbed simply by imbibing water.
2.Osmotic priming:
- Osmotic priming is soaking of seeds in the solutions containing container like:
- Mannitol
- Potassium nitrate (KNO3)
3.Solid matrix priming:
- Potassium chloride (KCL)
- Polyethylene glycol (PEG)
- Sodium chloride
Solid matrix priming involves the incubation of seeds in a solid, insoluble matrix-like vermiculite, diatomaceous earth, or highly water absorbent polymer with a limited amount of water, allowing for slow inhibition.
4.Bio-priming:
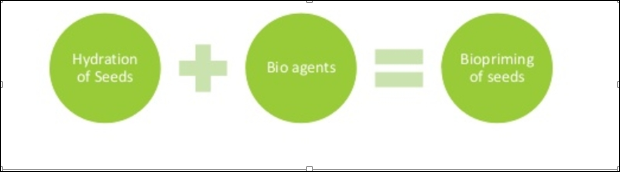
Bio-priming is the biological method of a seed treatment that refers to the combination of seed hydration (physiological aspects of disease control) and inoculation (biological aspects of disease control) of seed with beneficial organisms to protect seed.
Drying seeds after priming :
Seed dehydrator is used for drying the seeds. Slow drying at moderate temperatures is preferable. Seeds are redried to their actual weight for normal handling.
Writer : Bishal K.C.









